SOMA¶
Semantic Object Map (SOMA) package. SOMA can include objects, regions of interest (ROI) and trajectories. It is based on Mongodb for storing high-level data obtained from perceptual pipeline of a robot. The extracted data could be stored along with spatial and temporal information which can be later used for building high-level queries with spatio-temporal constraints.
Prerequisites¶
- MongoDB (>=2.6)
- ROS mongodb_store package
- ROS navigation stack (only map server)
- Qt5 (sudo apt-get install qtbase5-dev)
Getting started (general steps)¶
Start the ros core:
$ roscore
Launch the ROS datacentre:
$ roslaunch mongodb_store mongodb_store.launch db_path:=<path_to_db>
By default, the SOMA data are stored in
somadatadatabase. The collections under this database areobjectfor SOMA objects,roifor SOMA rois andmapfor 2D occupancy maps.
SOMA map manager¶
SOMA is based on the assumption that all the data are with respect to 2D global map frame. So it is mandatory to publish a 2D map using SOMA map manager before using SOMA. This node is used for storing, reading and publishing 2D map:
$ rosrun soma_map_manager soma_map_manager_node.py --mapname <map_name>
If there are any stored 2D occupancy maps in the datacenter, the name of the map could be inputted as an argument to the map manager. Alternatively, user can choose the map to be published from the outputted list. If there are no stored maps, it will wait for a 2D map to be published from map_server. Run the map_server with a 2D map:
$ rosrun map_server map_server <map.yaml>wheremap.yamlspecifies the map you want to load. After running themap_server, you should save the published map using theSOMA map manager.If you want to check the published map, start RVIZ, add a Map display type and subscribe to the
soma/maptopic:
$ rosrun rviz rviz
SOMA ROI manager¶
If you want to create SOMA ROIs, run the SOMA ROI manager:
$ rosrun soma_roi_manager soma_roi_node.py <config_name>
where
config_namedenotes an object configuration name. By default, the configuration filesoma_roi_manager/config/default.jsonis used to initialize the list of available ROI types. Alternatively, the following command can be used to use a different configuration file:$ rosrun soma_roi_manager soma_roi.py -t /path/to/config/file <config>
2D
mapinformation will be gathered fromsoma/map_infoservice ofSOMA map manager.In RVIZ, add an InteractiveMarker display type, and subscribe to the
/soma_roi/updatetopic:Add, delete, modify ROIs in RVIZ using the interactive marker and the context menu (right-mouse-click)
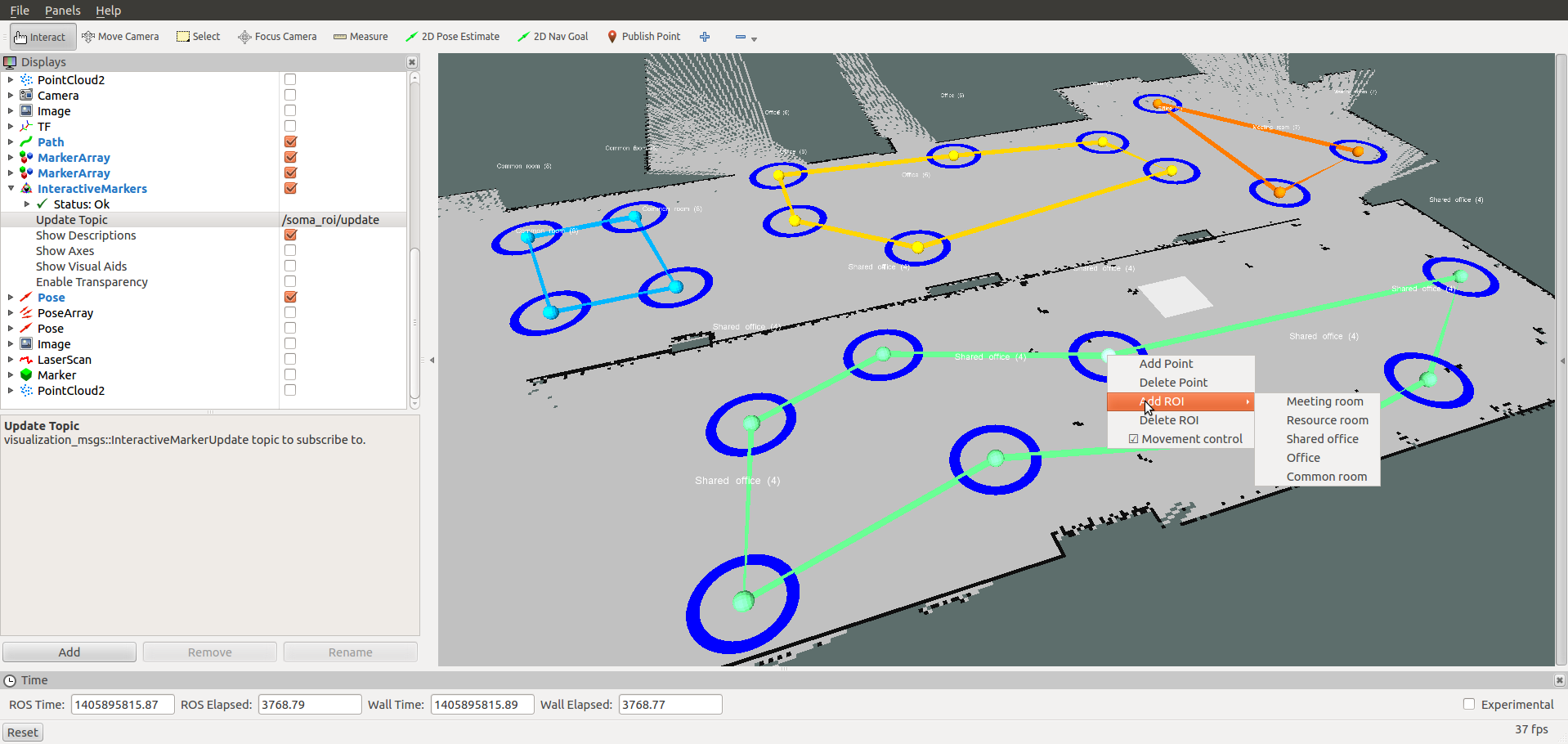
marker
ROS Services¶
The other nodes can communicate with SOMA using the SOMA service calls. In order to use these services, one should run the soma data manager: ## SOMA data manager 1. Run the soma data manager:
$ rosrun soma_manager data_manager_node.py
--object_collection_name <collection_name> --object_db_name <db_name>
The parameters db_name and collection_name are optional which
can be used to define the database and collection name for data storage.
SOMA query manager¶
Run the soma query manager:
$ rosrun soma_query_manager query_manager_node <object_db_name> <object_collection_name> <roi_db_name> <roi_collection_name>
By default the data is stored under default db and collections :
| object | ROI | map | |
|---|---|---|---|
| db_name | somadata | somadata | somadata |
| collection_name | object | roi | map |
Object insertion¶
One or multiple SOMA objects can be inserted using the SOMA service call
/soma/insert_objects. The unique mongodb ids and a boolean value are
returned. The boolean return value determines whether the request was
successfully completed or not. ### Object deletion One or multiple SOMA
objects can be deleted using the SOMA service call
/soma/delete_objects. The SOMA object ids are used for deletion. The
boolean return value determines whether the request was successfully
completed or not. ### Object update A SOMA object can be updated using
the SOMA service call /soma/update_object. The boolean return value
determines whether the request was successfully completed or not. ###
Object query SOMA objects could be queried using SOMA service call
/soma/query_objects. The query request should be filled according to
the spatio-temporal constraints. The results are returned based on the
query type and constraints. ### ROI query SOMA ROIs could be queried
using SOMA service call /soma/query_rois. The query request should
be filled according to the spatio-temporal constraints. The results are
returned based on the query type and constraints.
Original page: https://github.com/strands-project/soma/blob/indigo-devel/README.md