Task Executive¶
A set of nodes and libraries for defining and executing long-term task-level behaviour.
Overview¶
The task executor is the central element of the strands_executive
framework. It receives tasks from clients, queues them for execution,
then manages their execution and the required navigation between tasks.
This package provides two executors: the simple fifo_task_executor
which simply executes tasks in the order it receives them (ignoring
their timing constraints) and the scheduled_task_executor which uses
the scheduler
node
to create and maintain an execution schedule based on the time windows
of the tasks. This package also provides the task_routine Python
module which facilitates the creation of daily task routines with
repeating temporal structure.
Modules¶
For the task routine module see the description on the overview page, and the API documentation.
Runtime Dependencies¶
For the executive framework to function correctly, you must have the mongodb_store nodes running. These are used by the framework to store tasks with arbitrary arguments.
roslaunch mongodb_store mongodb_store.launch
or with path specifying, where should the db is stored:
roslaunch mongodb_store mongodb_store.launch db_path:=/...
Currently the task executive abstracts over navigation actions using the STRANDS topological navigation framework. Therefore you must have this framework running. For testing, or if you’re not running the full topological navigation system, you can run a simple simulated topological system with the following command:
roslaunch topological_utils dummy_topological_navigation.launch
This produces a map with 9 nodes: ChargingPoint in the centre, with
v_-2, v_-1 to v_2 running vertically and h_-2 to h_2
running horizontally, joining ChargingPoint in the middle.
Nodes¶
scheduled_task_executor.py¶
This node receives tasks via the services, schedules them for execution, then executes them in the order defined by the schedule.
Execution Status¶
When the executor is started, it will not start executing any tasks
until the execution status is set to True via a call to the
/task_executor/set_execution_status
(strands_executive_msgs/GetExecutionStatus) service. If execution
status is set to False then execution pauses, interrupting any
currently executing task.
Task Addition and Scheduling¶
Tasks are added using the add_task (single task) and add_tasks
(multiple tasks) services. All received tasks are added to a queue for
scheduling which is monitored by the executor. When then queue contains
tasks, the new tasks, plus the tasks already scheduled are sent to the
scheduler
node.
If a task is successfully created, this replaces the previous schedule
and execution continues. If scheduling fails then the newly added tasks
are dropped by the executor and the previous schedule is reinstated.
Adding new tasks does not interrupt the currently executing task.
Task Demanding¶
If a task should be executed immediately, the demand_task
(strands_executive_msgs/DemandTask) service can be used. This
interrupts the currently executing task and replaces it with the
demanded task. The schedule is then recreated to respect the execution
constraints of the demanded task, and, if possible the interrupted task
is included in this new schedule.
Interruptibility¶
By default the execution of tasks is interruptible (via actionlib
preempt). If you do not wish your task to be interrupted in these
condition you can provide the IsTaskInterruptible.srv service at the
name <task name>_is_interruptible, e.g.
do_dishes_is_interruptible from the example above. You can change
the return value at runtime as this will be checked prior to
interruption.
Here’s an example from the node which provides the wait_action.
class WaitServer:
def __init__(self):
self.server = actionlib.SimpleActionServer('wait_action', WaitAction, self.execute, False)
self.server.start()
# this is not necessary in this node, but included for testing purposes
rospy.Service('wait_action_is_interruptible', IsTaskInterruptible, self.is_interruptible)
def is_interruptible(self, req):
# rospy.loginfo('Yes, interrupt me, go ahead')
# return True
rospy.loginfo('No, I will never stop')
return False
Task Execution and Monitoring¶
When a task is executed it pass through two phases: navigation and
action execution. If the task has a start_node_id set then the
executor uses topological navigation to move the robot to this start
node. Before doing so it obtains an estimate of the travel time from the
topological_navigation/travel_time_estimator service. If the travel
time greatly exceeds this estimate, the topological navigation action is
preempted and the task execution is failed. If the
topological_navigation action reports anything but success on
completion then the task execution is failed. If it reports success then
the task moves on to the action execution phase. This phases triggers
the action server described by the task. If execution of the action
server greatly exceeds the max_duration of the task, it is preempted
and execution is considered failed. The overall execution state machine
is pictured below.
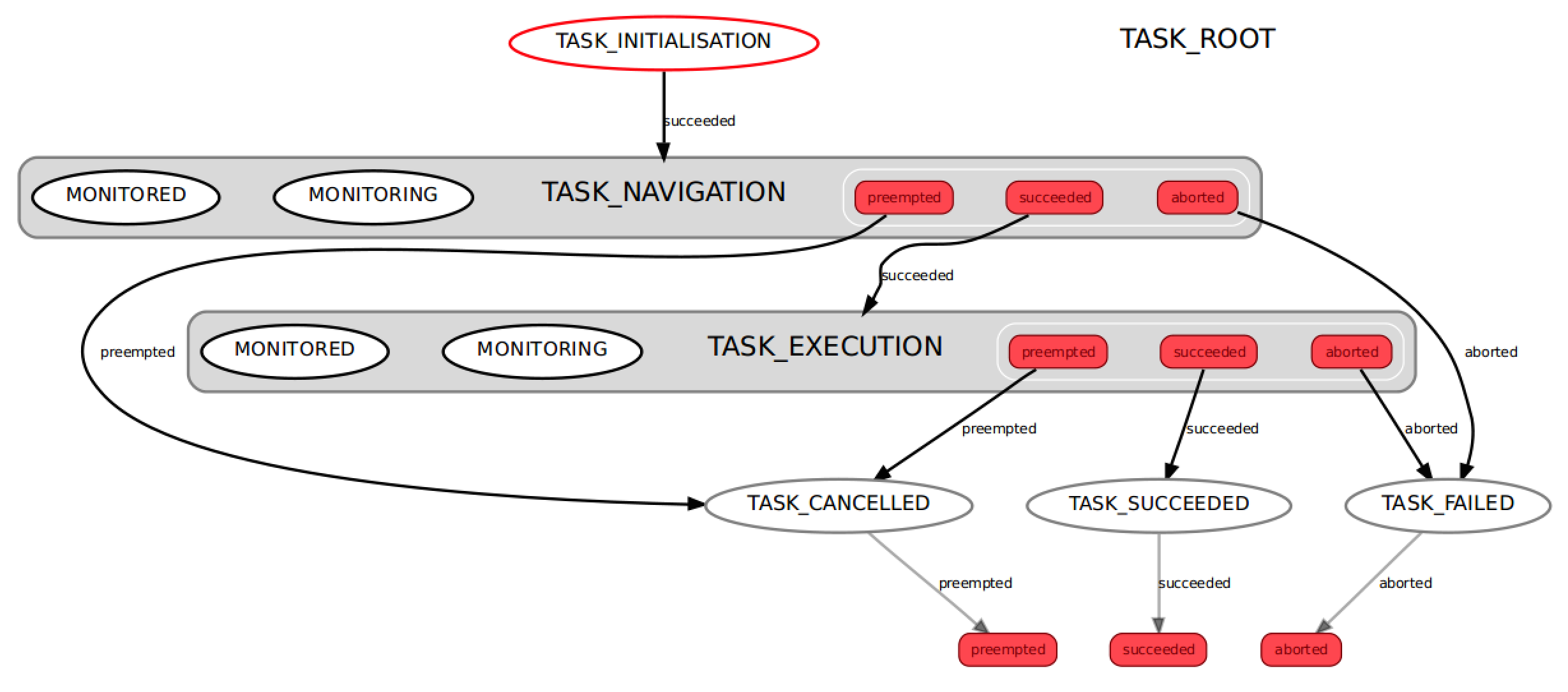
Task executor state machine
Services¶
task_executor/add_tasks
(strands_executive_msgs/AddTasks)
Add a list of tasks to be scheduled for execution.
task_executor/add_task
(strands_executive_msgs/AddTask)
Add a single task to be scheduled for execution.
task_executor/demand_task
(strands_executive_msgs/DemandTask)
Triggers the immediate execution of a task, interrupting the currently executing task.
task_executor/set_execution_status
(strands_executive_msgs/SetExecutionStatus)
Sets the execution status of the executor. Set to false to pause execution. Starts at false so much be set to true on start-up.
task_executor/get_execution_status
(strands_executive_msgs/GetExecutionStatus)
Gets the current execution status of the executor.
task_executor/clear_schedule (std_srvs/Empty)
Clears all tasks scheduled for execution. Cancels any active task.
task_executor/cancel_task
(strands_executive_msgs/CancelTask)
Removes the task with the given id from the schedule. If this task is currently executing, execution is interrupted.
task_executor/get_active_task
(strands_executive_msgs/GetActiveTask)
Gets the task which is currently executing.
Published Topics¶
task_executor/events
strands_executive_msgs/TaskEvent)
Events that happen as the task executor passes through its state machine for each task.
current_schedule
strands_executive_msgs/ExecutionStatus)
The list of upcoming tasks and what is currently being executed.
fifo_task_executor.py¶
A greatly simplified task executor that executes tasks in the order they
are added, and only supports task addition and very little else when
compared to the scheduled_task_executor.
schedule_status.py¶
Prints a summary of the current_schedule topic.
Original page: https://github.com/strands-project/strands_executive/blob/indigo-devel/task_executor/README.md